Dalam bahasa Indonesia kita tidak mengenal kalimat nominal. Namun didalam bahasa inggris kita tidak hanya menemukan kalimat verbal saja tetapi juga kita akan menemukan kalimat nominal. Misal untuk mengatakan “saya lapar” maka dalam bahasa inggris “They are hungry”.
Untuk mengetahui jenis kalimat itu apakah verbal atau nominal adalah dengan menemukan verb “be” (is, am, are, was, were, been). Jika kata kerja “be dkk” tersebut menjadi ordinary verb maka kalimatnya disebut kalimat nominal. Dan begitu sebaliknya akan dikatakan kalimat verbal jika "be dkk" bukan menjadi bukan menjadi ordinary verb dalam susunan kalimat.
Be dalam kalimat nominal akan selalu diikuti oleh 3 complements yaitu adjective, noun dan adverb entah itu dalam bentuk kata ataupun frase. Adapun rumusnya dapat disimak dibawah ini:
1. Simple Present dan Present Continuous
Rumus : S + is, am, are + 3C
Contoh
- are they at home?
- He is not a doctor.
- I am tired.
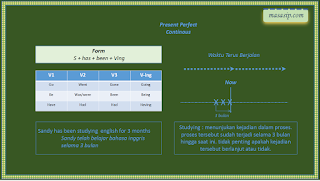
2. Present Perfect dan Present Perfect Continuous
Rumus : S + have, has + been + 3C
Contoh
- she has been here for 3 hours.
- They have not been there.
- Where have you been?
3. Simple Past dan Past Continuous
Rumus : S + was, were + 3C
Contoh
- I was a student of an english course
- We were not in hospital.
- Was mira scared of him?
4. Past Perfect dan Past Perfect Continuous
Rumus : S + had + been + 3C
Contoh
- She had been in the office when you arrived
- The students had not been in the class when the teacher came.
5. Simple Future dan Future Continuous
Rumus : S + will, shall + be + 3C
Contoh
- I will be rich
- We shall not be busy if we finish this duty today.
6. Future Perfect dan Perfect Continuous
Rumus : S + will, shall + have + been + 3C
Contoh
- we shall have been capable of understanding english.
- Shall i have been in the class before the teacher come?
7. Past Future dan Past Future Continuous
Rumus : S + would, should + be + 3C
Contoh
- we should be proud of him.
- We should not be angry with him.
8. Past Future Perfect dan Past Futre Perfect Continuous
Rumus : S + should, would + have + been + 3C
Contoh
- They would have been glad if they had had a good idea.
Everything would have been fine before we had had dinner last night.